Brazil Tax Calculations
In most VAT systems, the taxable basis of standard transactions is the gross amount of the goods and services supplied:
Taxable Basis = Gross Amount
But, under Brazilian tax law, the taxable basis is defined as the value of the operation, which is understood as the final price including taxes (grossed up).
Taxable Basis = Gross Amount + Taxes
This illustration compares basic VAT calculations with Brazil tax calculations:

Brazil Tax Authority Types
ONESOURCE Indirect Tax Determination supports the tax authority types in the table below. The final column shows the Calculation Methods that are associated with these authorities (for more information, see Brazil Calculation Methods).
|
Tax Authority Type |
Jurisdiction |
Description |
Calculation Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
|
IPI |
Federal |
Tax on Industrial Products. VAT system applicable to goods only. |
Brazil (Standard) or Inclusive Tax (Brazil only) |
|
ICMS |
State |
Tax on Movement of Goods and Services. It is a VAT system applicable to goods and certain services that are out of scope of ISS. |
Brazil (Standard) or Inclusive Tax (Brazil only) |
| ICMS-PF | State |
Brazil IMCS Trava PF Price. Taxable basis is calculated based on the manufacturers published price for each EAN code. This authority is used to contribute the Pauta Fiscal PF published price to the authority for which the adjusted taxable basis is calculated (i.e. ICMS Trava - Sao Paulo). |
Tax Substitution Modified Basis (Brazil Only) |
| ICMS-PMC | State |
Brazil ICMS Trava PMC Price. Taxable basis is calculated based on the maximum consumer price for each EAN code. This authority is used to contribute the Pauta Fiscal PMC published price to the authority for which the adjusted taxable basis is calculated (i.e. ICMS Trava - Sao Paulo). |
Tax Substitution Modified Basis (Brazil Only) |
|
ICMS-RD |
State |
Buyer and Seller liability for ICMS in the destination state of an interstate transaction, arising from the rate differential between the applicable interstate rate and the ICMS rate of the destination state. |
Rate Differential (Brazil Only) Rate Differential Modified Basis (Brazil Only) Brazil (Standard) Tax on Contributing Authorities |
|
ICMS-ST |
State |
Tax on the sale of goods as part of a specific segment of a product's lifecycle, including the anticipated markup of the manufacturer selling to a distributor or reseller. In addition to the standard Brazil authorities, these transactions also return the following:
The ICMS-ST and FCP-ST calculation is dependent on the IVA authority. |
Tax Substitution (Brazil Only) Tax Substitution Modified Basis (Brazil Only) |
|
ICMS-ST-CNAE |
State
|
Brazil ICMS CNAE Basis Adjustment. An adjusted taxable basis is calculated based on the CNAE code, which identifies a business practice within Brazil. This authority type is primarily used to calculate the ICMS-ST adjusted taxable basis in the Brazil state of Mato Grosso. |
Tax Substitution Modified Basis (Brazil Only) |
|
ICMS-ST-CNAE-IVA |
State |
Brazil ICMS CNAE IVA Basis Adjustment. An adjusted taxable basis is calculated based on the Imposto sobre Valor Agregado (value added tax). This authority type is primarily used to calculate the adjusted IVA ICMS-ST taxable basis in the Brazil state of Mato Grosso. |
Tax Substitution Modified Basis (Brazil Only) |
|
ISS |
Municipal |
Tax on Services. A cumulative tax system applicable to services that is defined by each municipality. |
ISS (Brazil only) |
|
IVA |
State |
The markup percent applied to the ICMS taxable basis to arrive at the taxable basis for ICMS-ST, where the corresponding state protocols apply. |
IVA (Brazil Only) |
|
FCP |
State |
Poverty Fund Combate. An ICMS additional rate, which applies on specific products depending on the state legislation. |
Inclusive Tax (Brazil only FCP (Brazil Only) |
|
FCP-ST
|
State |
Poverty Fund Combate. An ICMS-ST additional rate, which applies on specific products depending on the state legislation. |
FCP-ST (Brazil Only) Tax Substitution Modified Basis (Brazil Only) |
|
PIS |
Federal |
The Social Integration Program, and is defined as a social contribution. |
Brazil (Standard) or Inclusive Tax (Brazil only) |
|
COFINS |
Federal |
The contribution for the financing of Social Security. Defined as a social contribution. |
Brazil (Standard) or Inclusive Tax (Brazil only) |
|
II |
Federal |
Importation tax (duties). Determination provides this authority type as a custom authority template only. This authority is required to calculate taxes due on importation of goods. It is based on a gross amount equal to the Custom Value (price exclusive of taxes), the default treatment by ONESOURCE Indirect Tax Determination. You can override that assumption by using the calculation method of Inclusive (Brazil only). No standard rates or rules are provided for this authority type. Use the custom authority template provided by Determination, and establish custom rules and rates. For more information, see Rules. |
Brazil (Standard) |
The following sections describe aspects of transactions under Brazil tax authorities:
PIS and COFINS
These tax types have non-cumulative liability. Unlike cumulative liability, they allow deduction of input tax credits under certain conditions. In non-cumulative liability, companies must account for PIS and COFINS on a transaction basis, making them similar to value-added taxes.
Brazil business processes handle PIS and COFINS differently due to the special nature of these levies. Because PIS and COFINS are not technically considered indirect taxes, there is no requirement to print the PIS and COFINS tax amounts on an invoice, although they would be included in other tax documents. But under the non-cumulative regime, taxpayers are allowed to deduct input tax credits and must account for PIS and COFINS in every transaction.
Goods
On Brazilian tax invoices, the Product Amount is used for the supply of goods, indicating the value of the product. It includes all costs plus PIS, COFINS, and ICMS. IPI is not generally included in the Product Amount. For importation, the Customs Value applies instead.
Services
The Service Amount on a Brazilian tax invoice is used for the supply of services, indicating the value of the service. It includes all costs plus PIS, COFINS, and ISS.
Business Supply Flag
When used in a transaction involving a Brazil tax authority, the Business Supply flag indicates whether the supply is meant for final consumption or resale. For more information about the Business Supply flag, see Place of Supply of Services.
When the Business Supply flag is set to Yes (Resale), the IPI tax amount is not included in the taxable basis of ICMS: ICMS Taxable Basis = Cost + ICMS + PIS + COFINS. The Business Supply flag must be set to Yes (Resale) for Determination to calculate ICMS-ST. When the Business Supply flag is set to No (Final Consumption), the IPI tax amount is included in the taxable basis of ICMS:
- ICMS: ICMS Taxable Basis = Cost + ICMS + PIS + COFINS + IPI
- ICMS-ST Taxable Basis: (Product Amount (Gross Amount) + (Gross + PIS + COFINS + IPI + ICMS)) * Adjusted IVA%)
- Adjusted IVA: [(1+'Original IVA') x (1 - 'Interstate Rate of Ship From State')/(1 - 'Internal Rate in Destination State')] -1
-
ICMS End Consumer: ICMS Taxable Basis = Cost + ICMS_RATE SHIP TO+ PIS + COFINS + IPI
The Buyer registration must be empty for ICMS End Consumer to apply.
Pauta Fiscal for ICMS and ICMS-ST
Brazilian tax authorities that implement state-level Pauta Fiscal rely on one or more of the following processes published by the government:
- PF: Manufacturers Published Price
- PMC: Maximum Consumer Price
These prices define the adjusted taxable basis for ICMS and ICMS-ST.
Sao Paulo and Mato Grosso handle Pauta Fiscal differently from other states:
-
Sao Paulo: PF and PMC apply to both intrastate and interstate transactions, and both published prices are typically used to contribute to the adjusted taxable basis for ICMS and ICMS-ST. The ICMS-PF Authority Type is used to contribute the PF published price to the ICMS Trava Sao Paulo authority taxable basis. The ICMS-PMC Authority Type is used to contribute the PMC published price to the ICMS Pauta Sao Paulo authority taxable basis. After the adjusted taxable basis for both ICMS Trava Sao Paulo and ICMS Pauta Sao Paulo authorities are calculated, Determination compares the two taxable basis to determine which is a larger value:
- If the ICMS Trava Sao Paulo authority taxable basis is greater than the ICMS Pauta Sao Paulo taxable basis, the ICMS Trava Sao Paulo taxable basis is contributed to the ICMS-ST Sao Paulo authority.
- If the ICMS Pauta Sao Paulo authority taxable basis is greater than the ICMS Trava Sao Paulo taxable basis, the ICMS Pauta Sao Paulo taxable basis is contributed to the ICMS-ST Sao Paulo authority.
-
Mato Grosso: This state does not use the government published prices (PF and PMC). Instead, Mato Grosso uses discount percentages to adjust the taxable basis for ICMS and ICMS-ST based on the National Code of Economic Activity for the Comprehensive Guaranteed ICMS Program or the Simplified Estimation Regime.
- Comprehensive Guaranteed ICMS Program: Determination uses a percentage to calculate the taxable basis and tax amount on the authority that uses the ICMS-ST-CNAE Authority Type and ICMS-ST-CNAE-IVA Authority Type. The tax amounts of both corresponding Mato Grosso authorities are compared to each other. The smaller of the two tax amounts is the ICMS-ST tax result.
- Simplified Estimation Regime: Determination uses a percentage to calculate the taxable basis and tax amount on the authority that uses the ICMS-ST-CNAE Authority Type.
If your business uses the Simplified Estimation Regime, you must include the term SIMPLE as the value in the End Use field to apply the logic for this regime.
Brazil Calculation Methods
The Brazil calculation methods provided by ONESOURCE Indirect Tax Determination determine the applicable formulas to apply for tax calculation in each case (for example, importation or domestic; goods or services; or inclusive or exclusive). The specific formulas for calculation of taxes due on Brazil importation are included in all calculation methods. See the table below for descriptions of the calculation methods.
Except for the Inclusive (Brazil only) calculation method, ONESOURCE Indirect Tax Determination assumes that the gross amount does not include the related tax amount when product rules are applied that use the Brazil (Standard), ISS (Brazil only), Tax Substitution (Brazil Only), IVA (Brazil Only), or Importation (PIS or COFINS) calculation methods.
These methods also evaluate other taxes that are applicable to the same transaction to determine if their respective tax amounts have been included in the gross amount.
|
Calculation Method |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Brazil (Standard) |
This is the recommended calculation method to use when other special cases do not apply. You should use this method in IPI, PIS, COFINS, and ICMS authorities when you pass the net price (product value before taxes) as a gross amount. When you pass the price with tax included as gross amount, you should use the Inclusive (Brazil only) calculation method.
|
| New Brazil (Standard) |
This is an extension of the Brazil (Standard) method but excludes ICMS from Taxable Basis of PIS and COFINS. This can be applied to both buyer and seller side scenarios for both resale and consumption/capitalization of assets scenarios. |
|
ISS (Brazil only) |
Use this calculation method for ISS authorities as an alternative to Brazil (Standard), although the calculated results are the same. |
|
COFINS Importation |
Use this calculation method for COFINS authorities for importation transactions as an alternative to Brazil (Standard), although the calculated results are the same. |
|
PIS Importation |
Use this calculation method for PIS authorities for importation transactions as an alternative to Brazil (Standard), although the calculated results are the same. |
| New PIS COFINS (Brazil only) |
This is an extension of the PIS COFINS (Brazil only) method but excludes ICMS from Taxable Basis of PIS and COFINS. Since the IPI tax amount charged by the seller is taken as a cost by the buyer, PIS and COFINS also should have taxable basis increased to allow recovery of those taxes completely. Therefore, this method is only applicable to buyer side transactions for both resale and consumption/capitalization of assets scenarios. |
|
Inclusive Tax (Brazil only) |
An inclusive tax affects calculation of all Determination-supported Brazilian taxes.
For more information about inclusive taxes, see Inclusive Taxes. For information about setting the calculation method on any desired rules to an inclusive tax type, see Workbench Inclusives. |
| New Inclusive Tax (Brazil only) |
This is an extension of the Inclusive Tax (Brazil only) method but excludes ICMS from Taxable Basis of PIS and COFINS. This can be applied to both buyer and seller side scenarios for both resale and consumption/capitalization of assets scenarios. |
|
Tax Substitution (Brazil Only) |
This calculation method applies to ICMS-ST and refers to tax on the anticipated mark-up to a distributor or reseller. |
| Tax Substitution Modified (Brazil Only) | This calculation method applies to ICMS-ST and refers to tax on the anticipated mark-up to a distributor or reseller, with a modified basis to apply the grossed up concept on ICMS-ST results. This is in accordance with Convenio 51/2017. |
|
IVA (Brazil Only) |
This calculation method supplies the IVA mark-up percentage for both intrastate and interstate transactions.
|
|
Rate Differential (Brazil Only) |
This calculation method is used to determine buyer and seller liability for ICMS in the destination state of an interstate transaction, due to the difference in the interstate ICMS rate and local ICMS rate in the destination state. It also includes IPI on ICMS calculation basis. |
| Rate Differential Modified (Brazil Only) |
This calculation method is used to determine buyer and seller liability for ICMS in the destination state of an interstate transaction, due to the difference in the interstate ICMS rate and local ICMS rate in the destination state. Includes a modified basis to apply the grossed up concept on ICMS-ST results in accordance with Convenio 51/2017. |
| FCP-ST (Brazil Only) |
Use this calculation method for FCP-ST authorities. |
Use Cases
The following Workbench use cases show tax calculation for several supported types of tax. Note that inclusive taxes are marked by the I in the IT (Inclusive Tax) column of the output.
Before implementing a particular tax type or calculation method, you should test samples of your transactions in the Workbench.
- Gross amount does not include taxes.
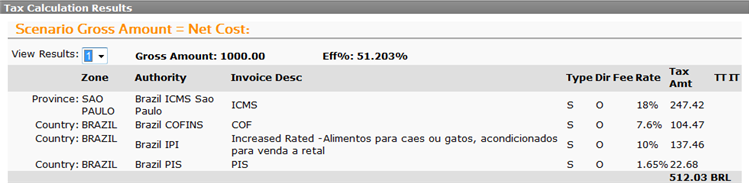
- Gross amount is inclusive of PIS, COFINS and ICMS. A custom rule for each one of these authorities was used with a calculation method of Inclusive Tax (Brazil only).

- Importation of goods into Brazil. A custom authority, with rules and rates, was set up for II - Importation Tax (Imposto de Importação).

- ICMS tax substitution for goods sold within a single state (intrastate).

- ICMS tax substitution for goods sold between states (interstate).
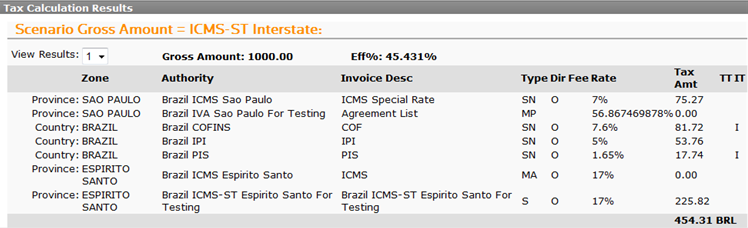
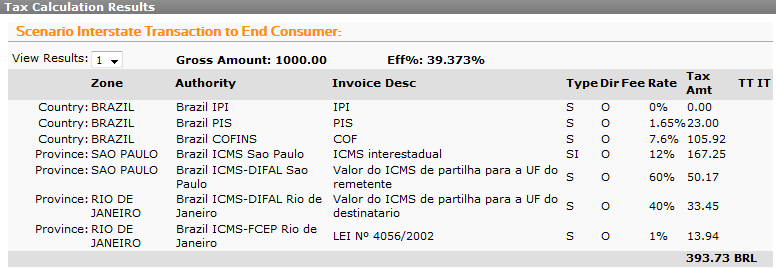
-
ICMS rate differential for a sale between states to an end consumer (interstate).
Audit Considerations
All the authorities in the examples above are audited, but there are some special considerations for IVA and ICMS (Ship To). Rates are returned in Audit for these authorities, and taxable basis and tax amount are zero:
|
Authority |
Tax Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
IVA |
MP |
The Tax Substitution Markup Percent. |
|
ICMS (Ship To) |
MA |
The ICMS internal rate in the Ship To for Markup Adjustment Percentage. |
|
FCP (Ship To) |
MA |
The FCP internal rate in the Ship To for Markup Adjustment Percentage. |